CI/CD - Secure Deployment in GCP Cloud Run / App Engine using Cloud Build and Secret Manager - Part 1
Table of contents
- Introduction
- STEPS
- Create a repository in GCP
- Download a starter spring project
- Update DemoApplication.java code
- Add cloudbuild-cr.yaml in the root folder
- Add Dockerfile in the root folder
- Add jdbc.user, jdbc.password and jdbc.url secrets in Secret Manager
- Create a gcr.io Artifact repository for Docker images
- Now create a Cloud Build trigger using cloudbuild-cr.yaml
- Running the trigger will deploy the Cloud Run application
- Next Step is to deploy into App Engine
- Create the app first
- Add app.yaml in root folder
- Add cloudbuild-app.yaml in root folder
- Add an "appprop" secret key in Secret Manager and upload a file with the following keys
- Run the trigger and it would deploy the application in App Engine as a default service.
- Conclusion
Introduction
In this article, you will see how you can use CI/CD pipeline using Cloud Build and Secret Manager in GCP to deploy the application in Cloud Run or App Engine. In Part 2 we will connect to a MySQL database using Private IP.
STEPS
Create a repository in GCP
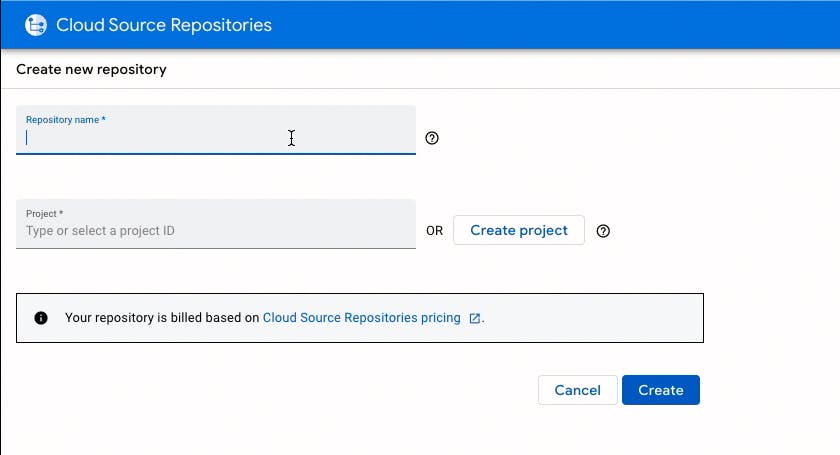 Open the repository in Cloud Shell editior.
Open the repository in Cloud Shell editior.
Download a starter spring project
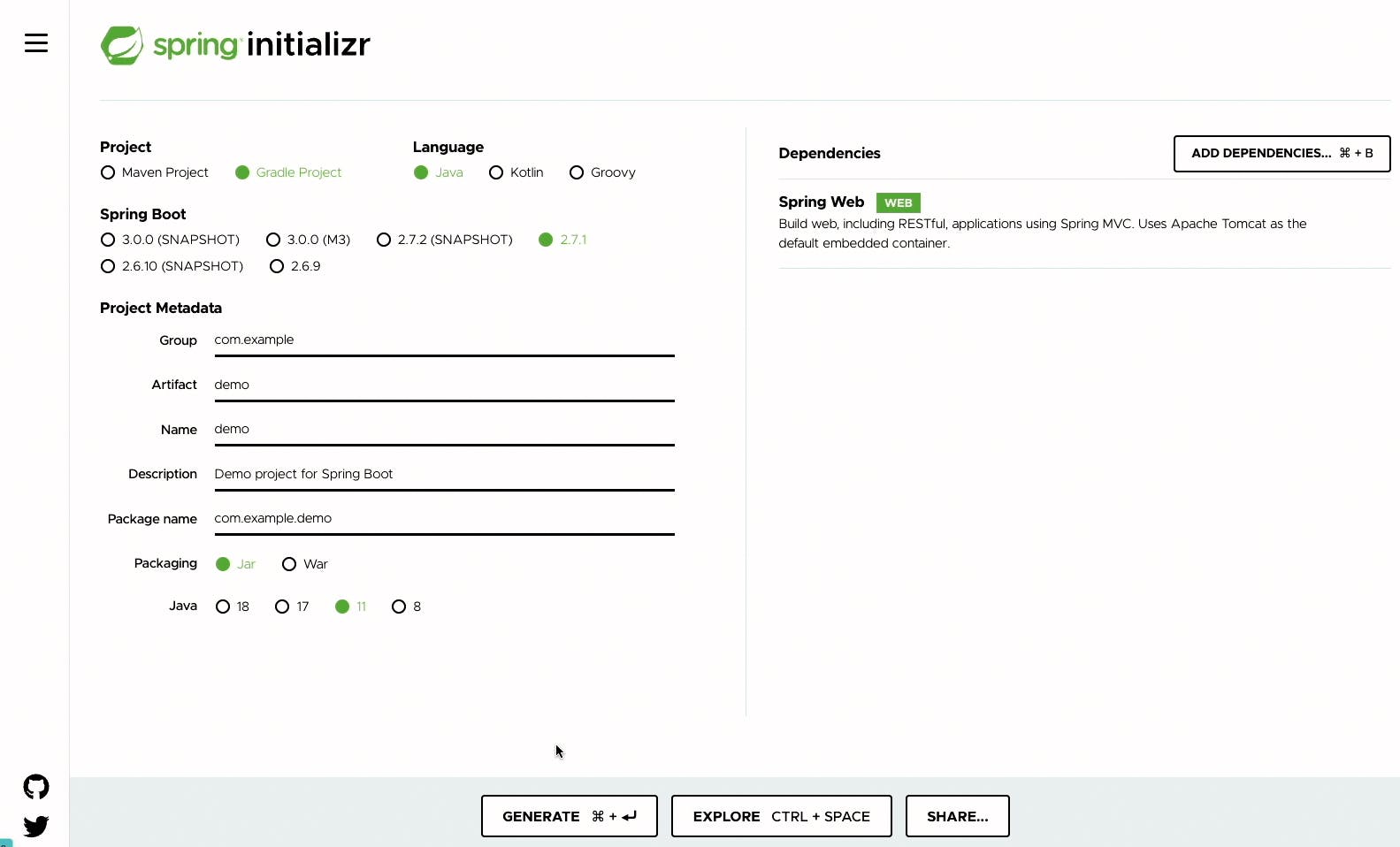
Upload the demo.zip into the Cloud shell and unzip the file into the repository folder in Cloud Shell.
Update DemoApplication.java code
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class DemoApplication {
@Autowired
Environment env;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
@RequestMapping
public String home(){
return "hello gcp:" +"jdbcuser=" + env.getProperty("jdbc.user")+ " jdbcpassword=" + env.getProperty("jdbc.password")+ "jdbcurl=" + env.getProperty("jdbc.url");
}
}
We have added environment properties in the code to check the values passed.
Add cloudbuild-cr.yaml in the root folder
steps:
- name: gradle:7.4.2-jdk17
entrypoint: gradle
args: ["assemble"]
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker
args: ["build", "-t", "us-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/gcr.io/springbootgcp:$COMMIT_SHA", "--build-arg=JAR_FILE=build/libs/springbootgcp-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar", "."]
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker
args: [ "push", "us-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/gcr.io/springbootgcp:$COMMIT_SHA" ]
- name: 'gcr.io/google.com/cloudsdktool/cloud-sdk'
entrypoint: gcloud
args: ['run', 'deploy', 'springbootgcpcr', '--image', "us-docker.pkg.dev/$PROJECT_ID/gcr.io/springbootgcp:$COMMIT_SHA" , '--allow-unauthenticated','--port=8080','--region', 'us-central1' ,'--set-secrets=--jdbc.user=jdbcuser:latest, --jdbc.password=jdbcpassword:latest, --jdbc.url=jdbcurl:latest']
timeout: "1600s"
options:
logging: CLOUD_LOGGING_ONLY
Cloud build runs three steps: assemble, build, push and finally run.
Add Dockerfile in the root folder
FROM openjdk:17
ARG JAR_FILE=build/libs/springbootgcp-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
COPY ${JAR_FILE} app.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar"]
Add jdbc.user, jdbc.password and jdbc.url secrets in Secret Manager
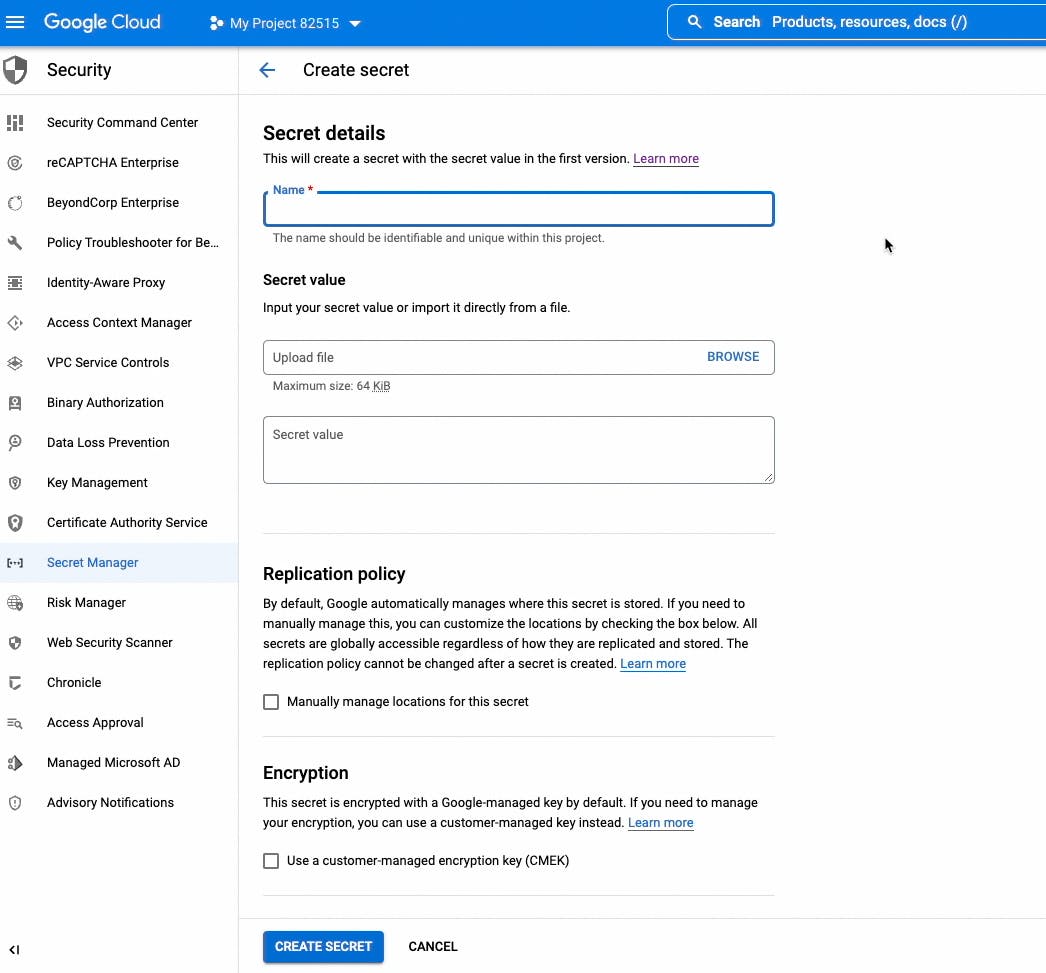 Give developer and cloudbuild service account "Secret Manager Secret Accessor" role.
Give developer and cloudbuild service account "Secret Manager Secret Accessor" role.
Create a gcr.io Artifact repository for Docker images
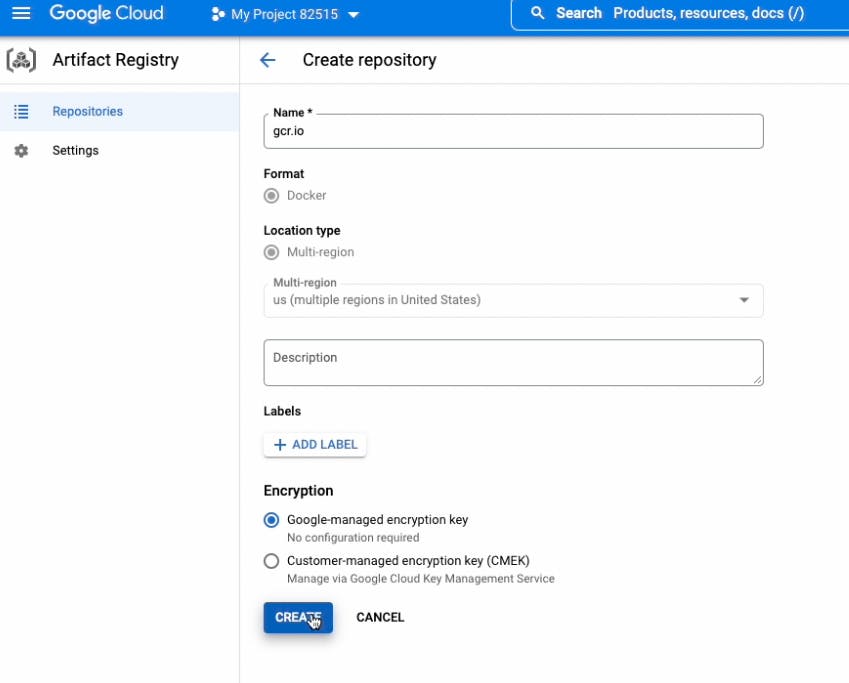
Now create a Cloud Build trigger using cloudbuild-cr.yaml
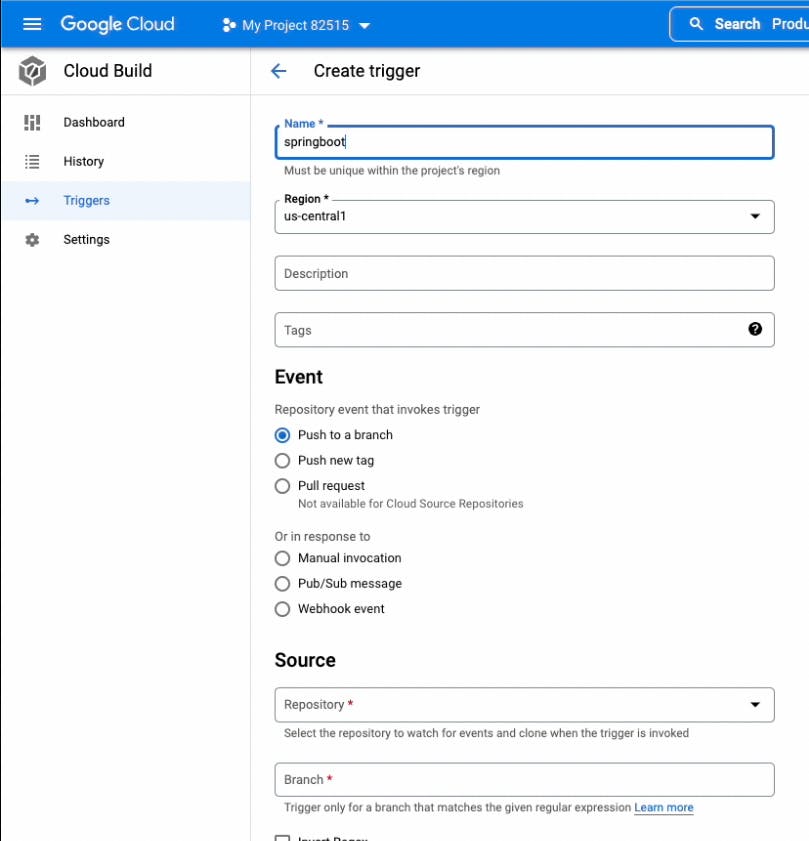
Running the trigger will deploy the Cloud Run application
When you run the first time you may see an error in the build but it deploys the application properly in Cloud Run.
Next Step is to deploy into App Engine
Create the app first
gcloud app create --region=us-central
Add app.yaml in root folder
runtime: java17
entrypoint: java -jar app.jar
Add cloudbuild-app.yaml in root folder
steps:
- name: gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud
entrypoint: 'bash'
args: [ '-c', "gcloud secrets versions access latest --secret=appprop > src/main/resources/application.properties" ]
- name: gradle:7.4.2-jdk17
entrypoint: gradle
args: [ "assemble" ]
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud"
entrypoint: bash
args: ['-c', 'mkdir appdeploy && cp /workspace/app.yaml /workspace/appdeploy/ && cp /workspace/build/libs/springbootgcp-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar /workspace/appdeploy/app.jar ' ]
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud"
entrypoint: gcloud
args: ['app', 'deploy','./appdeploy/app.yaml' ]
timeout: "1600s"
options:
logging: CLOUD_LOGGING_ONLY
Add an "appprop" secret key in Secret Manager and upload a file with the following keys
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=password
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://10.11.0.3:3306/testdb
Run the trigger and it would deploy the application in App Engine as a default service.
Conclusion
I have posted a detailed youtube video of this article. Also, the full source code is available on GitHub. App Engine doesn't have direct integration with Secret Manager currently that's why I had to use bash script. The next step is to build on this tutorial and add a MySql connection using Private IP.
